Deep Learning Firewall
A firewall system utilizing deep learning to filter malicious network traffic
Deep Learning Firewall
The Deep Learning Firewall project focuses on developing a firewall system that uses deep learning algorithms to intelligently filter and block malicious network traffic. This project enhances traditional firewall capabilities by incorporating advanced machine learning techniques to predict and prevent cyber-attacks.
Technologies Used
Backend
Language: Python
Frameworks: TensorFlow, Keras, Flask
Frontend
Framework: Flask
Dataset
Name: CSIC HTTP Attacks Dataset
Model Architecture
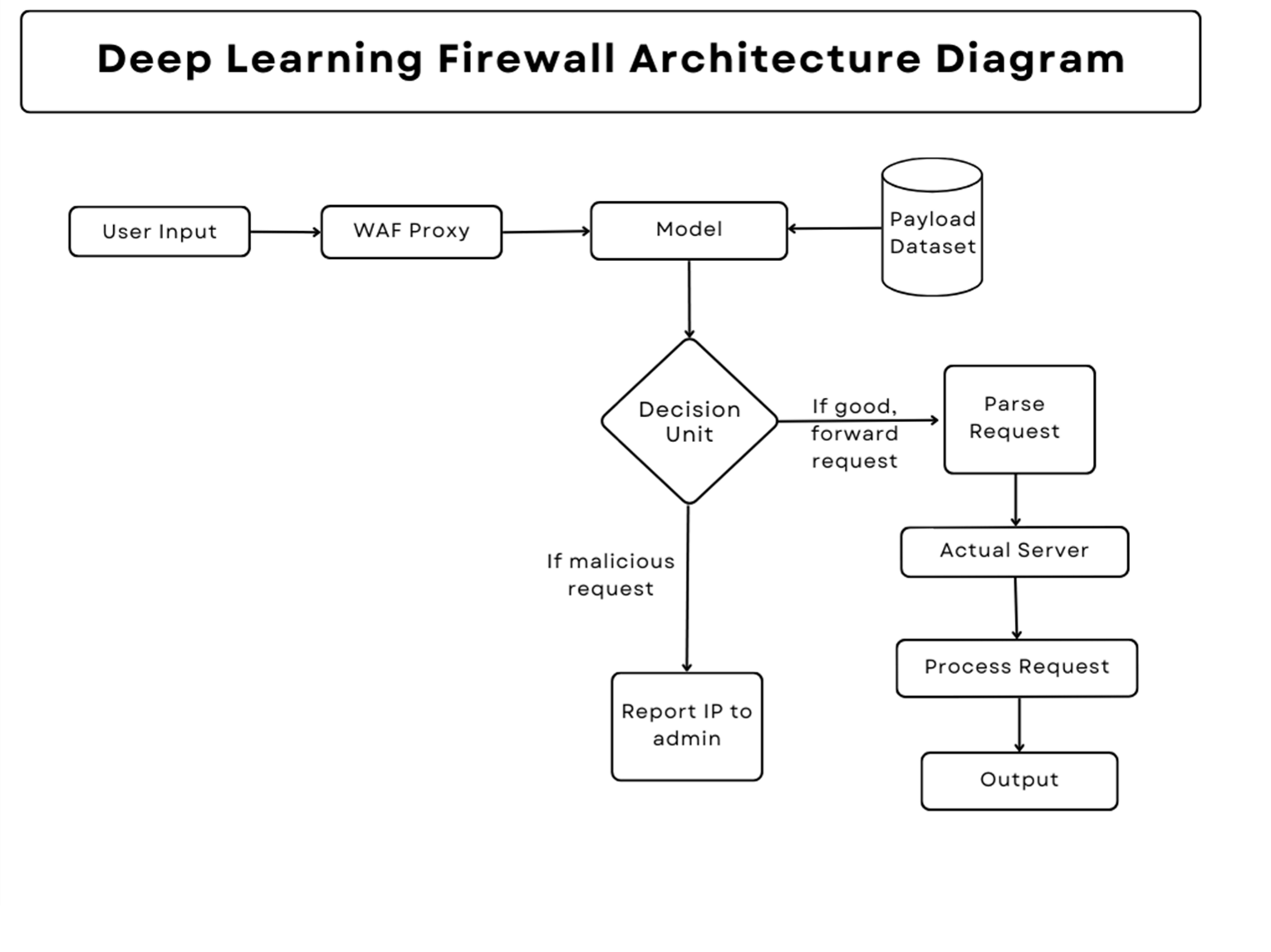
Modular Description
Data Pre-processing
Dataset: HTTP DATASET CSIC 2010
- Produced by the Spanish Research National Council (CSIC).
- Includes 36,000 normal traffic samples and over 25,000 malicious traffic samples.
- Contains various attacks such as SQL injection, buffer overflow, and information gathering queries.
Approach:
- The raw dataset consists of HTTP requests with URL encoding.
- Challenges include extracting useful features due to the large number of escape characters (
%).
Model Training
Embedding Layer:
- Converts each character of the input HTTP request sentence into a 128-dimensional vector.
Architecture:
- Significant dimensional reduction occurs at the second max-pooling layer (498:1 at K=2).
- This approach greatly reduces the number of fully connected elements in subsequent layers.
- Minimizes GPU memory requirements for training.
Connection of WAF
Integration:
- The trained model is connected with a sample web application using the Flask framework.
- A proxy is established between the model and the application to evaluate incoming requests.
Malicious Query Detection
Process:
- Malicious requests to the sample application are detected and blocked.
- User IP addresses of the blocked requests are logged and displayed in the WAF panel.
Illustrations

Figure 1.1: Output when a normal request is applied
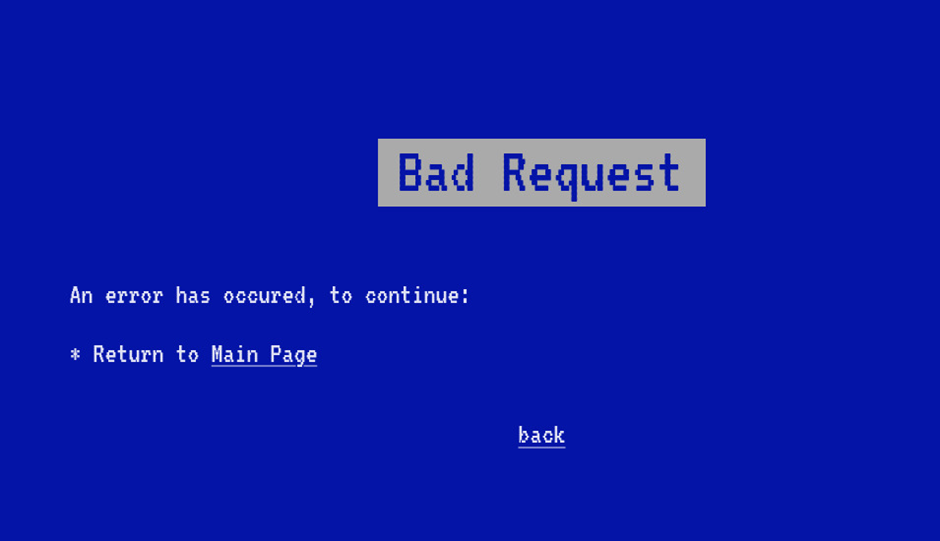
Figure 1.2: Output when a malicious request is applied
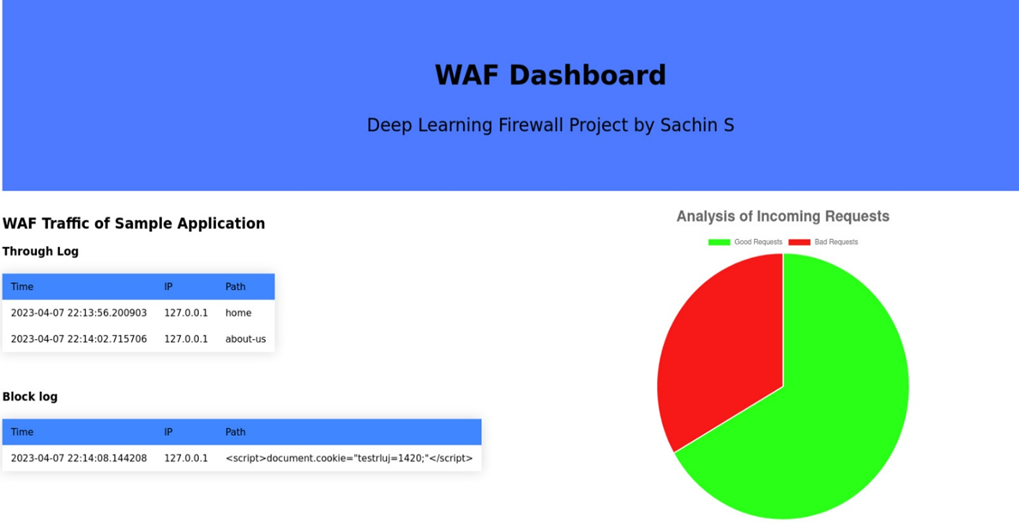
Figure 2.1: WAF Dashboard for the sample web application
Future Extensions
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- The WAF can be enhanced to function as an IDS for large-scale networks to protect against major cyber-attacks.
- Blockchain Protection
- Modify the firewall to provide advanced protection for blockchain applications, including bitcoin mines and decentralized apps (DApps).
- Antivirus Integration
- Leverage the model to classify different HTTP attack types and integrate with antivirus software to block malicious actors.
Note: The source code for this project is confidential and not publicly available as it is part of academic research. For more information or assistance, feel free to reach out.